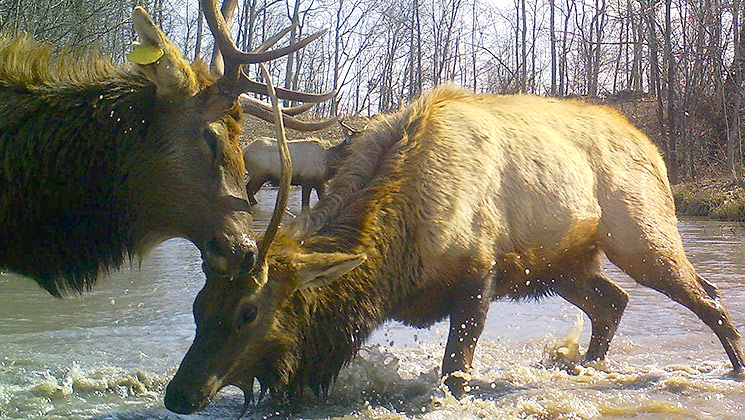
Hunters are the leaders in conservation, and the Rocky Mountain Elk Foundation (RMEF) is a group that has been paramount in the reintroduction and conservation of elk across North America. From Pennsylvania in 1985 to Wisconsin in 1995, Kentucky in 1997, Tennessee in 2000, Ontario in 2001, the Great Smoky Mountains National Park in 2002, Missouri in 2011 and now Virginia in 2014, RMEF is responsible for many successful elk restorations.
But without the help of partners including state fish and wildlife departments and local volunteers, and donations from around the country, RMEF efforts would be fruitless. A combination of these efforts is exactly what was necessary for the reintroduction of elk to Virginia last year. The project, originally spearheaded by the Virginia Department of Game and Inland Fisheries (VDGIF), was met with initial resistance from the Virginia Farm Bureau as farmers worried about potential fence and crop damage as well as the spread of disease to existing cattle herds. VDGIF chose Buchanan County as the drop location because its vast reclaimed mine lands provided the least amount of agricultural risk, and Buchanan was the only county that didn’t initially oppose the reintroduction. The agency coordinated with Buchanan County, RMEF and the Kentucky Department of Fish and Wildlife Resources (KDFWR) and today Buchanan, Dickenson and Wise counties all are included in the Virginia restoration, which adds up to 1,200 square miles of elk country.
After the successful soft release of 71 elk (a process by which elk are slowly acclimated to a release site within large fenced-in areas prior to release) from neighboring Kentucky between 2012 and 2014, VDGIF moved into a monitoring phase. Still to be finalized is a 10-year elk management plan that, once the herd reaches 400 strong, will include hunting as a management tool. According to VDGIF, this might occur within three years. For guidance, Virginia will look toward existing programs in Kentucky, Tennessee and Pennsylvania.
As with any big game, especially a species that is rare to an area, poaching is a concern. “There is always that possibility, but with the interest and support of the citizens Buchanan County of the elk restoration project and the value of these majestic animals to the future of the county, we do not expect any problems,” said VDGIF deputy bureau director Bob Ellis. “We also have an enforcement presence in the area that is highly regarded and works to protect all of our wildlife resources in the county.”
A project like this is not cheap; the entire process cost around $500,000, most of which was generated by RMEF. But money is not the only essential element of a successful elk reintroduction. Volunteers are key.
“Without James Coleman and several other volunteers just as dedicated as him, we could never make this happen,” said RMEF volunteer Leon Boyd. “I think volunteers to a project such as this are critical. I have 37 committee volunteers in our RMEF chapter.”
“The RMEF volunteers, and in particular Mr. Leon Boyd, have been influential in the success of the restoration project here in Virginia,” said Ellis. “If it wasn’t for their passion and dedication in volunteering their time and labor to the project, we would not have achieved the success we enjoy today.”
Through the cooperative efforts of these groups and many local volunteers, Virginia elk are currently thriving—so much so that even yearlings are breeding.
According to an excerpt from North American Elk: Ecology and Management, by D. Toweill and J. Thomas (Smithsonian Institution Press), yearling pregnancies among elk are not common. “Puberty and conception rates are strongly related to body weight,” wrote the authors. “About half of elk cows will come into estrus for the first time at a threshold weight of about 70 percent of the mature weight. In well-nourished populations first estrus normally occurs in the fall of the second year of life, particularly common in farmed animals, whereas in free-ranging populations a smaller proportion of yearlings have full-term pregnancies.”
The Virginia elk pregnancies are due to good nutrition. Part of that comes from the high nutrient content found in the reclaimed mine lands of Buchanan County, but food plots planted by volunteers also contribute to the herd’s health. The Virginia herd is around 100 strong now, with 20 calves born in 2014 and possibly 50 more this year, according to Boyd.
Will the Virginia elk stay in Virginia? Considering Buchanan County is near the borders of West Virginia and Kentucky, the long-term answer is, probably not. But one can hope they grow in number and spread enough throughout the Old Dominion that migration to neighboring states isn’t a concern. “Elk could move into West Virginia, back into Kentucky or into neighboring counties in Virginia,” said Ellis. “However, with the release process used in our reintroduction, what we called a soft release, animals acclimated to the release site before being released, and we felt pretty confident the animals would stay near the site. Also, the habitat work done by the RMEF volunteers has proven to be invaluable in keeping the elk in proximity of the release area. As more animals populate through natural reproduction, I’m sure we will see general movement in the area of elk.”
“Buchanan was the only county that spoke in favor of the stocking,” said Boyd. “It is very possible that elk can go to West Virginia, Kentucky or anywhere they wish because they are free-ranging. We have seen the majority of the animals stay within a few miles of the release area. Just this morning I saw 54 elk.”
All of this leads one to wonder whether the volunteers so vital to the project’s success also value their own opportunities to hunt these majestic animals in the future. Would Leon Boyd hunt the elk, for instance, if he won a tag?
“If I was lucky enough to win a Virginia elk tag, I would hope to be able to auction it off to help keep the elk habitat here in Virginia,” he said. That’s an amazing testament to the dedication of the project’s volunteers, and a prime example as to why the program has been such a success.