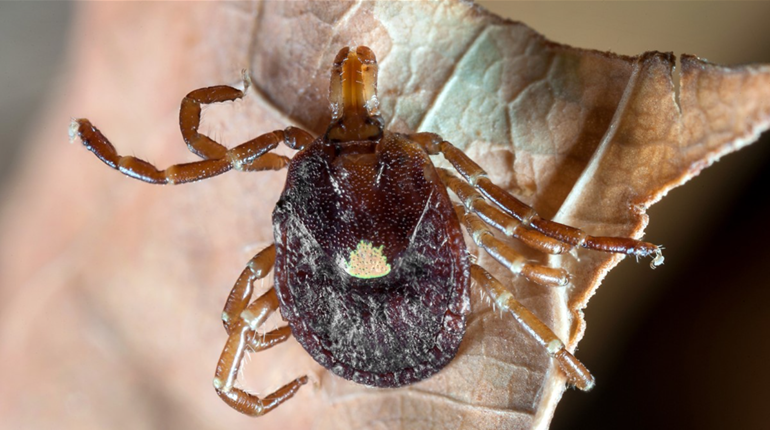
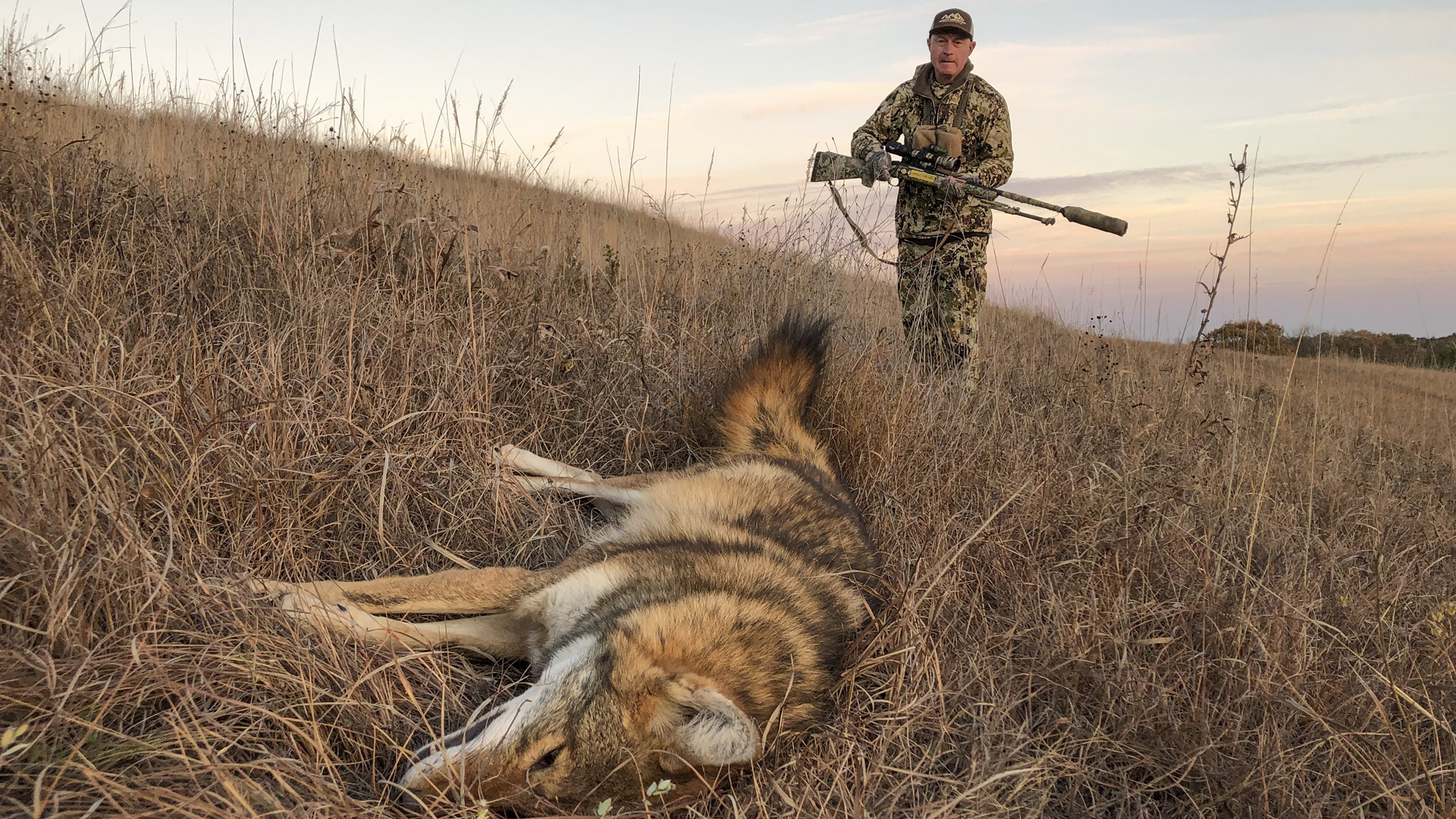
After Lyme disease reared its ugly head in 1975 and subsequently spread throughout much of the country, it changed how we care for our gundogs. We vaccinate them against the disease. We check them for ticks after every hunt. And we apply monthly tick repellents such as Frontline and Advantix. Yet, if you own enough dogs over the course of enough years, it's likely one or even a few will contract Lyme. And let's not forget that you yourself are susceptible.
The funny thing about Lyme is how little we still know about it. We don't even know for certain how it came about, but it's been assumed that overpopulated deer herds facilitated a boom in the tick population and, therefore, the Lyme epidemic. But a new study out of the University of California-Santa Cruz defies the conventional wisdom, suggesting that the spread of coyotes across the northeastern United States had far more to do with the tick-Lyme boom than deer.
According to the study, the removal of wolves by settlers of the northeastern United States paved the way for coyotes to spread east (wolves do not tolerate coyotes in their territory). And, as coyotes have entered the northeastern United States, which is outside their traditional range, they have in turn taken a toll on red fox populations.
"A new top predator has entered the Northeast and has a strong impact on the ecosystem," study researcher Taal Levi said in a statement. Coyotes kill a lot of foxes and, more importantly, he said, " ... Foxes often don't build dens when coyotes are around."
So, what's this have to do with Lyme? According to the study, fewer red foxes have allowed their favorite foods—namely mice, shrews and chipmunks—to greatly expand their populations. And such rodents are just as susceptible to carrying and spreading deer ticks as deer are.
What do you think? Could it be that the current scourge of Lyme-carrying deer ticks was caused by something other than deer?